Powering What’s Next
#WeAreConnectriq a Complete EV Changing Solution Company
Smart EV Charging Solutions, Tailored to Fit Your Needs
At Connectriq, we offer a Turnkey EV Charging Solutions
Residential Societies
Business Park & Corporates
Protected Charging
(EV Charging for Members of Housing & complexes)
New Construction
Retails Sector
Hospital Sector
Public Charging
(EV Charging for Public)
Our Products

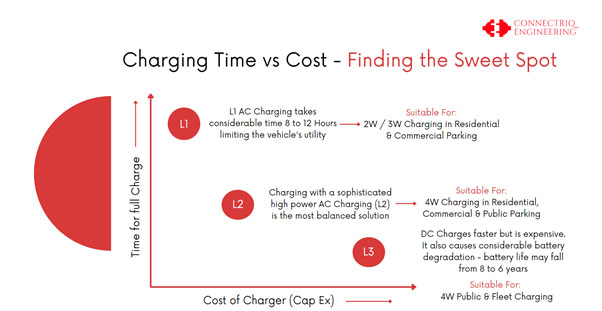
Difference L1, L2, L3
Charging at home or on the go? Learn the difference between
Level 1, Level 2, Level 3 charging
Click to expand below>

Why L2?
Click to expand below>

3. Different L2 Options
Click to expand below>
-
Difference L1, L2, L3


Charging at home or on the go? Learn the difference between
Click to expand below
Level 1, Level 2, Level 3
charging. -
Why L2?


Charge your EV 3 to 5 times faster with a Level 2 charger – and get back on the road!
Click to expand below -
Different L2 Options

Explore Level 2 charging options available for your EV.
Click to expand below
Difference between Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 Charging


LEVEL 1 CHARGING
230 Volt-
 Provides charging through a standard (three-prong) 230V plug that comes with your EV. The other end is simply plugged directly into your EV
Provides charging through a standard (three-prong) 230V plug that comes with your EV. The other end is simply plugged directly into your EV -
 Doesn’t require installation of additional charging equipment
Doesn’t require installation of additional charging equipment -
 Time from fully depleted to fully charged: average 8 – 16+ hours
Time from fully depleted to fully charged: average 8 – 16+ hours -
 Recommended in urgent cases when you have low battery charge and cannot drive to a public station or access an AC wallbox at home.
Recommended in urgent cases when you have low battery charge and cannot drive to a public station or access an AC wallbox at home.
LEVEL 2 CHARGING
230 Volt Wall-mounted Charging Station-
 Provides charging through a 230V outlet which allows charging 3 to 4 times faster than L1 Charger – depending on the acceptance rate of your specific model and the charger
Provides charging through a 230V outlet which allows charging 3 to 4 times faster than L1 Charger – depending on the acceptance rate of your specific model and the charger -
 Requires the installation of a dedicated EV charging wallbox, which should be fitted by a trained / licensed electrician
Requires the installation of a dedicated EV charging wallbox, which should be fitted by a trained / licensed electrician -
 Time from fully depleted to fully charged: average 4-10+ hours depending on vehicle
Time from fully depleted to fully charged: average 4-10+ hours depending on vehicle  Ideal for residential & business parks or if you have a garage or driveway in which it can be positioned
Ideal for residential & business parks or if you have a garage or driveway in which it can be positioned

LEVEL 3 CHARGING
High-powered DC Fast-charge Station-
 Provides charging power above 50kW through a voltage above 450V and current up to 125A
Provides charging power above 50kW through a voltage above 450V and current up to 125A -
 Delivers DC energy bypassing the on-board charger - the quickest way to charge an electric vehicle
Delivers DC energy bypassing the on-board charger - the quickest way to charge an electric vehicle -
 Time from fully depleted to fully charged in about 30 - 90 minutes
Time from fully depleted to fully charged in about 30 - 90 minutes -
 Ideal for Public Charging
Ideal for Public Charging -
 Use of DC Charge should be kept to a minimum in order to help prolong high-voltage battery life
Use of DC Charge should be kept to a minimum in order to help prolong high-voltage battery life
Why Level 2?

Charge your EV 3 to 5 times faster with a Level 2 charger - and get back on the road!
Level 2 chargers allow you to charge your electric car in just a few hours while you sleep, work, enjoy a meal, or spend time with your family. A level 2 charger safely delivers AC power to your electric vehicle or plug-in hybrid so you’re always “fueled up” and ready to go.
Different L2 Options

Explore Level 2 charging options available for your EV.
Level 2 charging refers to the voltage that the electric vehicle charger uses (230 volts). Level 2 chargers come in a variety of amperages typically ranging from 30 amps to 48 amps. The two most common Level 2 chargers are 30 and 48 amps, which also may be referred to as 7.2 kW and 11 kW respectively. These two amperages are the most common because they match the onboard charger (OBC) on many of the current electric vehicles.
- Depending on the amperages, the difference between Level 2 chargers could be significant in charging times.
- Explore your options for both 16 and 30 amp chargers in our online store.
FAQs
Why do I need a charger?
EVs come equipped with cords and equipment that allow them to be plugged into conventional 230-volt outlets that are standard in your home or parking lot. However, EV owners can also purchase advanced, Level 2 chargers that will cut charging time in half, depending upon OBC of the EV. When considering home charging options, please consult with a licensed electrical contractor (LEC) as modifications to your home’s electrical wiring will likely be needed.
EVs can also be charge at public stations currently being installed across the country.
How often do I need to charge an EV?
It depends on the battery size of the vehicle, how energy-efficient your vehicle is, and, of course, your driving habits & traffic conditions.
Recent electric vehicles have ranges of over 220 – 350 kms, with batteries that can store from 30 to 45 or more kilowatt-hours (kWh). An average EV gets 7-10 km per kWh, so a 45-kWh battery has a range of somewhere between 315 and 450 kms, depending on how efficient the car is at using energy.
Do I have to charge my EV 100% every time?
EV manufacturers recommend you keep your battery charged between 20% and 80% of charge, which extends the lifetime of the battery. Only charge your battery up to 100% when you plan on going on a long trip.
It’s also recommended that you leave your vehicle plugged in if you’re going away for an extended period of time.
How long does it take to charge an EV at home?
Charging using a standard 230-volt outlet (3.3 kW) will give your battery around 20 – 22 kms of range per hour. If you drive 50 kms a day, it’ll take around 3 hours to recharge your battery to the level it was before you started your day.
Most EV drivers charge their vehicles overnight at home, while they’re sleeping. Note that charging speeds also depends on weather.
How long does it take to charge at a public charging station?
Public EV charging stations commonly have Level 2 chargers, which are normally 7.2 kW or 11 kW. A Level 3 charger (also known as a DC Fast Charger) can charge a 30 kWh EV from 0% to 100%, between 45 to 90 minutes, depending on rating of charger used.
Either way is longer than it does to refuel a HSD / petrol tank, but you don’t always need to refuel your EV to 100%. Many EV drivers refuel at public charging stations only enough to get them to their destination if they have the ability to charge overnight at home or at a hotel.
Is it cheaper to charge an EV than to fuel a petrol / HSD car?
Even if you only charge at the more expensive DC fast chargers, electricity is always cheaper than petrol / HSD. And it’s also cleaner.
The cheapest place to charge your vehicle is at businesses or workplaces that offer free charging. Second to that is charging at home, where electricity on average costs between Rs 7 to Rs 10 /kWh. Over the course of the car’s lifetime, the cost savings can make owning an EV cheaper than a petrol-powered car, even if the purchase price is significantly higher.
What happens if my battery runs out of charge?
Most electric vehicles will give you a warning when your battery is running low. When your charge gets dangerously low, your EV is likely to shift into economy mode. This reduces the maximum speed you can drive and sets regenerative braking to its highest level.
When your EV’s display says your battery is down to zero, it’s not really down to no electrons. It’s down to zero usable battery capacity. Your EV’s battery management system maintains a reserve supply of electrons to protect the battery from degradation.
In short, if you’ve never run out of petrol / HSD, you’re not likely to run out of electricity either.
How much maintenance do electric vehicles require?
Electric vehicles have 90% fewer moving parts and rely on regenerative braking, meaning there is less overall wear and tear. No fluids, no significant brake wear, and no exhaust system mean less ongoing repair and upkeep.
Connect with us
Our Contact
-
Email Address
connectriq.engineering@gmail.com
-
Call Us
+91 9820 150 406
-
Address
Connectriq Engineering Services LLP, Makwana Road, Marol, Andheri (east), Mumbai – 400059


